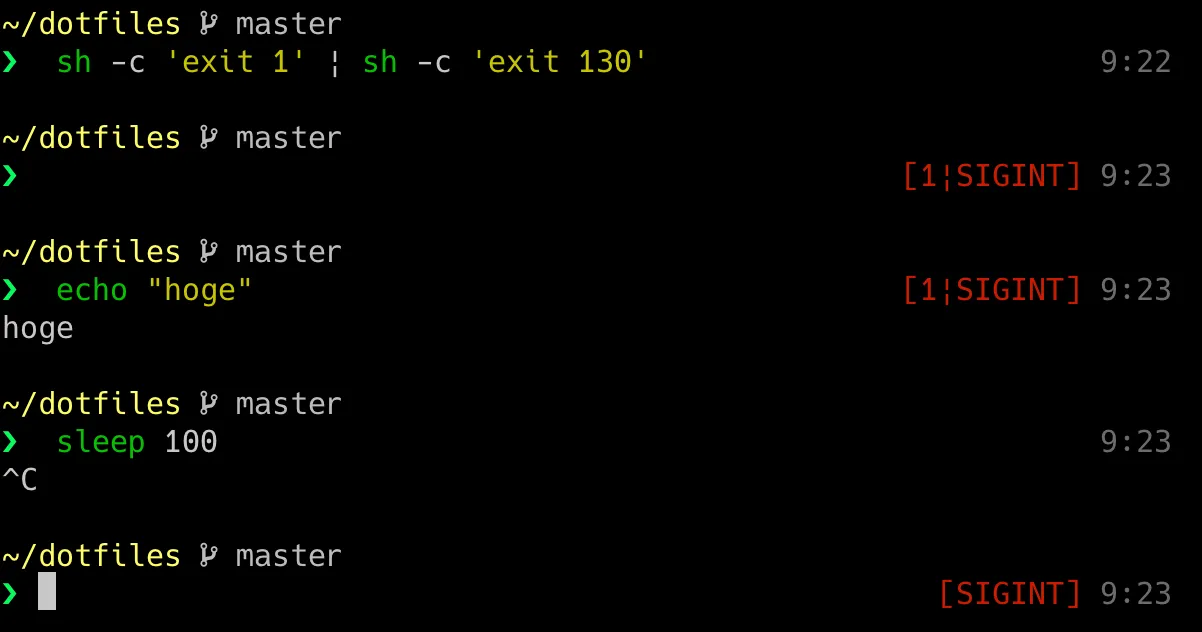
こんな感じで右プロンプトに直前のコマンドの結果を出力する(0 のとき以外)ようにした。
スクリプトとその説明
スクリプト全体を折りたたんで載せておく。
zshスクリプト
__signal_code_string() {
local ret=""
for STATUS in $__save_pipestatus;
do
# man signal
case $STATUS in
0 ) ;;
129) ret="${ret}|SIGHUP" ;; # terminate process terminal line hangup
130) ret="${ret}|SIGINT" ;; # terminate process interrupt program
131) ret="${ret}|SIGQUIT" ;; # create core image quit program
132) ret="${ret}|SIGILL" ;; # create core image illegal instruction
133) ret="${ret}|SIGTRAP" ;; # create core image trace trap
134) ret="${ret}|SIGABRT" ;; # create core image abort program (formerly SIGIOT)
135) ret="${ret}|SIGEMT" ;; # create core image emulate instruction executed
136) ret="${ret}|SIGFPE" ;; # create core image floating-point exception
137) ret="${ret}|SIGKILL" ;; # terminate process kill program
138) ret="${ret}|SIGBUS" ;; # create core image bus error
139) ret="${ret}|SIGSEGV" ;; # create core image segmentation violation
140) ret="${ret}|SIGSYS" ;; # create core image non-existent system call invoked
141) ret="${ret}|SIGPIPE" ;; # terminate process write on a pipe with no reader
142) ret="${ret}|SIGALRM" ;; # terminate process real-time timer expired
143) ret="${ret}|SIGTERM" ;; # terminate process software termination signal
144) ret="${ret}|SIGURG" ;; # discard signal urgent condition present on socket
145) ret="${ret}|SIGSTOP" ;; # stop process stop (cannot be caught or ignored)
146) ret="${ret}|SIGTSTP" ;; # stop process stop signal generated from keyboard
147) ret="${ret}|SIGCONT" ;; # discard signal continue after stop
148) ret="${ret}|SIGCHLD" ;; # discard signal child status has changed
149) ret="${ret}|SIGTTIN" ;; # stop process background read attempted from control terminal
150) ret="${ret}|SIGTTOU" ;; # stop process background write attempted to control terminal
151) ret="${ret}|SIGIO" ;; # discard signal I/O is possible on a descriptor (see fcntl(2))
152) ret="${ret}|SIGXCPU" ;; # terminate process cpu time limit exceeded (see setrlimit(2))
153) ret="${ret}|SIGXFSZ" ;; # terminate process file size limit exceeded (see setrlimit(2))
154) ret="${ret}|SIGVTALRM";; # terminate process virtual time alarm (see setitimer(2))
155) ret="${ret}|SIGPROF" ;; # terminate process profiling timer alarm (see setitimer(2))
156) ret="${ret}|SIGWINCH" ;; # discard signal Window size change
157) ret="${ret}|SIGINFO" ;; # discard signal status request from keyboard
158) ret="${ret}|SIGUSR1" ;; # terminate process User defined signal 1
159) ret="${ret}|SIGUSR2" ;; # terminate process User defined signal 2
* ) ret="${ret}|${STATUS}";;
esac
done
if [ ${#ret} -eq 0 ]; then
echo ""
else
echo "[${ret[2,-1]}]"
fi
}
__left-prompt() {
local dir="%F{11}%~%f"
local next="%F{47}❯%f "
if [ `git rev-parse --is-inside-work-tree 2> /dev/null` ]; then
local branch_name=`git rev-parse --abbrev-ref HEAD 2> /dev/null`
local branch="%F{250} ${branch_name}%f"
echo -e "\n${dir} ${branch}\n${next}"
else
echo -e "\n${dir}\n${next}"
fi
}
__right-prompt() {
local time="%F{242}%T%f"
local cmd_status="%F{1}`__signal_code_string`%f"
echo "${cmd_status} ${time}"
}
precmd() {
__save_pipestatus=("${pipestatus[@]}")
PROMPT=`__left-prompt`
RPROMPT=`__right-prompt`
}初歩的なプロンプト作成の方法はzsh プロンプトをカスタマイズするに書いたので省略する。
__signal_code_string()
$pipestatus の情報が保存された配列 $save_pipestatus に基づいて、いい感じの文字列を生成している。
実装については後述。
__left-prompt()
左のプロンプトを作成する関数。
現在ディレクトリ dir、git のブランチ情報 branch の情報の文字列を作成している。
__right-prompt()
右のプロンプトを作成する関数。
現在時刻 time、pipestatuscmd_status の情報の文字列を作成している。
precmd()
プロンプトを生成する。
$pipestatus の内容はスクリプト内のコマンドでも書き変わってしまうので __save_pipestatus に保存しておく。
僕は最初これに気が付かないで「あれー」ってやっていた...
ちなみに、この保存方法だけど、
__save_pipestatus=$pipestatusにしちゃうと __save_pipestatus が配列として保存できないので、
__save_pipestatus=("${pipestatus[@]}")にする必要があった。
$pipestatus の情報の加工
__signal_code_string() が行っているもの。
まず、終了ステータスについてだが、これらはWikipedia/終了ステータス#bashから引用すると、
| 終了ステータス | 意味 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 一般的なエラー |
| 2 | ビルトインコマンドの誤用 |
| 126 | コマンドを実行できなかった(実行権限がなかった) |
| 127 | コマンドが見つからなかった |
| 128 | exit に不正な値を渡した(例えば浮動小数点数) |
| 128+n | シグナル n で終了 |
| 255 | 範囲外の終了ステータス |
どこまで同じかわからないけど、少なくとも 128+n = シグナル n で終了 は zsh でも同じだった。
シグナルについては man signal でそれぞれの数値がどのような意味を持つのか確認できる。
一部を抜粋するとこんな感じである。
...
are simply discarded if the process has not requested otherwise. Except for the SIGKILL
and SIGSTOP signals, the signal() function allows for a signal to be caught, to be ignored,
or to generate an interrupt. These signals are defined in the file <signal.h>:
Name Default Action Description
1 SIGHUP terminate process terminal line hangup
2 SIGINT terminate process interrupt program
3 SIGQUIT create core image quit program
...僕の実装ではシグナル n は対応する Name に、それ以外の終了コードは数値として文字列にして結合している。
最後に、作った文字列を返すところ、
if [ ${#ret} -eq 0 ]; then
echo ""
else
echo "[${ret[2,-1]}]"
fiについて。
zsh では文字列も配列と同じように長さの取得やインデックスアクセスができた。
${#ret} で文字列 ret の長さを取得して処理を分岐、${ret[2,-1]} で ret から 1 文字目を取り除いた文字列を echo している。